

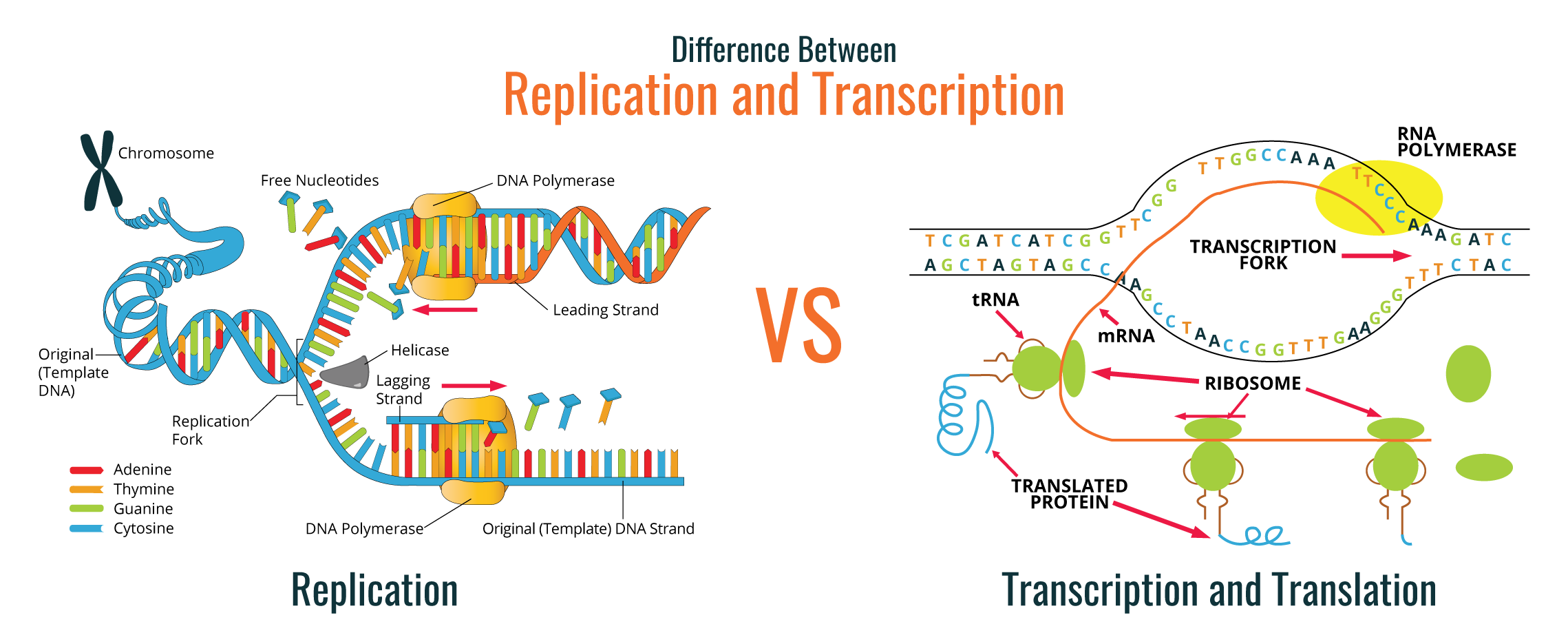
RNA polymerase binds to a sequence of DNA called the promoter, found near the beginning of a gene. You can learn more about the details of each stage (and about how eukaryotic transcription is different) in the stages of transcription article. Here, we will briefly see how these steps happen in bacteria. Transcription of a gene takes place in three stages: initiation, elongation, and termination. RNA transcript: 5'-UGGUAGU.-3' (dots indicate where nucleotides are still being added at 3' end) DNA template: 3'-ACCATCAGTC-5' RNA transcript: 5'-UGGUAGU.-3' (dots indicate where nucleotides are still being added at 3' end) The template DNA strand and RNA strand are antiparallel. It synthesizes the RNA strand in the 5' to 3' direction, while reading the template DNA strand in the 3' to 5' direction. RNA polymerase synthesizes an RNA strand complementary to a template DNA strand. Specifically, RNA polymerase builds an RNA strand in the 5' to 3' direction, adding each new nucleotide to the 3' end of the strand. The main enzyme involved in transcription is RNA polymerase, which uses a single-stranded DNA template to synthesize a complementary strand of RNA. RNA transcript (acting as messenger RNA): 5'-AUGAUCUCGUAA-3' Polypeptide: Met-Ile-Ser-STOP RNA transcript (acting as messenger RNA): 5'-AUGAUCUCGUAA-3'Ĭoding strand: 5'-ATGATCTCGTAA-3' Template strand: 3'-TACTAGAGCATT-5' RNA transcript: 5'-AUGAUCUCGUAA-3' The other strand, the coding strand, is identical to the RNA transcript in sequence, except that it has uracil (U) bases in place of thymine (T) bases.įor a protein-coding gene, the RNA transcript contains the information needed to synthesize a polypeptide (protein or protein subunit) with a particular amino acid sequence. One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary RNA transcript. In transcription, a region of DNA opens up. Eukaryotic transcripts need to go through some processing steps before translation into proteins. For a protein-coding gene, the RNA copy, or transcript, carries the information needed to build a polypeptide (protein or protein subunit). The goal of transcription is to make a RNA copy of a gene's DNA sequence. Transcription is the first step in gene expression, in which information from a gene is used to construct a functional product such as a protein. In biology, transcription is the process of copying out the DNA sequence of a gene in the similar alphabet of RNA. Transcription is something we do in our everyday lives, and it's also something our cells must do, in a more specialized and narrowly defined way. Or maybe you took notes in class, then rewrote them neatly to help you review.Īs these examples show, transcription is a process in which information is rewritten. Have you ever had to transcribe something? Maybe someone left a message on your voicemail, and you had to write it down on paper. Transcription is controlled separately for each gene in your genome. In eukaryotes, RNA molecules must be processed after transcription: they are spliced and have a 5' cap and poly-A tail put on their ends. Transcription has three stages: initiation, elongation, and termination. Transcription is performed by enzymes called RNA polymerases, which link nucleotides to form an RNA strand (using a DNA strand as a template). It involves copying a gene's DNA sequence to make an RNA molecule. Transcription is the first step in gene expression.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
